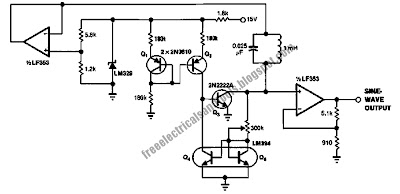
This is a circuit for precision oscillator that is the basic design using a voltage to frequency converter and based on op amp LM131. Basically, this IC, like any V/F converter, is a precision relaxation oscillator that generates a frequency linearly proportional to the input voltage. As might be expected, the circuit has a capacitor, CL, with a saw tooth voltage on it. This is the figure of the circuit.

The general description about this circuit is the circuit is a feedback loop that keeps this capacitor charged to a voltage very slightly higher than the input voltage, VIN. If VIN is high, CL discharges relatively quickly through RL, and the circuit generates a high frequency. If Vin is low, CL discharge slowly, and the converter puts out a low frequency. When CL discharges to a voltage equal to the input, the comparator triggers the one-shot. The one-shot closes the current switch and also turns on the output transistor. With the switch closed, current from the current source recharges CL to a voltage somewhat higher than the input. Charging continues for a period determined by RT and CT. At the end of this period, the one-shot returns to its quiescent state and CL resumes discharging. [Schematic’s source: National Semiconductor, Inc].

The general description about this circuit is the circuit is a feedback loop that keeps this capacitor charged to a voltage very slightly higher than the input voltage, VIN. If VIN is high, CL discharges relatively quickly through RL, and the circuit generates a high frequency. If Vin is low, CL discharge slowly, and the converter puts out a low frequency. When CL discharges to a voltage equal to the input, the comparator triggers the one-shot. The one-shot closes the current switch and also turns on the output transistor. With the switch closed, current from the current source recharges CL to a voltage somewhat higher than the input. Charging continues for a period determined by RT and CT. At the end of this period, the one-shot returns to its quiescent state and CL resumes discharging. [Schematic’s source: National Semiconductor, Inc].